Old people are riddled with many diseases? Nutritional support that can never be ignored

Writing expert: Zheng Peifen, Zhejiang Hospital, Clinical Nutrition Department, Chief Physician, Department Director.
According to the definition of WHO, two or more chronic non-communicable diseases coexist in the same person, which is referred to as comorbidity, coexistence of multiple chronic diseases or coexistence of multiple diseases. At present, comorbidity includes not only common chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease and tumor, but also senile syndrome or senile health problems, such as falls, weakness, sleep disorder, malnutrition, urinary incontinence, delirium, depression and drug addiction.
Comorbidity among the elderly is very common. At present, the prevalence rate of comorbidity among people over 65 years old in China is 60%, and the proportion of comorbidity among elderly inpatients is as high as 91.36%. Comorbidity will lead to prolonged hospitalization, increased risk of multiple drugs and adverse events, and increased medical expenses, which seriously threatens the physical and mental health and life safety of the elderly in China.[1] .
The incidence of malnutrition or malnutrition in the elderly with comorbidity is higher.
According to the data of prospective and multi-center survey in China, about 10.14% of hospitalized elderly patients are malnourished, and 46.42% are at nutritional risk. The incidence of malnutrition and nutritional risk increases obviously with age.[2]. The high nutritional risk rate of the elderly in the community is 48.4%[3]. According to the survey data of nutritional problems of elderly patients with comorbidity in a 3A hospital in Anhui, 68.5% of the elderly patients with comorbidity and multiple drugs are at nutritional risk and 15.7% are malnourished.[4].
Causes of comorbid malnutrition
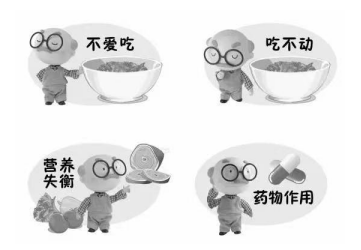
Elderly patients with comorbidity have degraded their own body functions, and at the same time, energy consumption is increased due to disease state and surgery, and their eating and digestive abilities are weakened due to braking, pain, and the need for multiple drugs, which is prone to malnutrition or malnutrition risks. The risk of malnutrition and malnutrition will lead to the increase of daily medication. Comorbidity and malnutrition/malnutrition risk problems interact.
Harm of comorbid malnutrition
Malnutrition in the elderly population seriously affects the treatment and prognosis of diseases. Malnutrition can not only affect the immune function, drug efficacy, disease or postoperative recovery effect, but also lead to the decline of multi-system function, which is easy to cause infection or make it difficult to control. In addition, poor outcomes caused by malnutrition, such as sarcopenia, cognitive impairment, falls, etc., will also cause weakness or promote the progress of weakness in elderly comorbid patients.
Oral nutritional supplement (ONS) has brought many benefits to the elderly with comorbidity.
1. ONS can improve the nutritional status of the elderly with comorbidity, which has a positive effect on the treatment of chronic diseases and the prognosis of patients.
For a long time, Chinese medical circles have regarded nutrition as a supplement and support, and regarded nutrition as a dispensable auxiliary. In the past 30 years, nutrition research has become a research hotspot. The dual functions of nutrition in significantly improving clinical outcomes and significantly saving medical expenses have been recognized more and more. People’s understanding of the importance of nutrition "treatment" has deepened day by day. Some experts even suggested that the last way to treat chronic diseases is "nutrition treatment". Nutritional therapy plays an important role in maintaining the normal metabolism of cells, supporting the function of tissues and organs, regulating the function of immune system, participating in the physiological function of the body and repairing the structure of tissues and organs.
The results of Lancet multi-center research show that compared with providing standard nutrition for hospital kitchens according to patients’ appetite, early ONS nutrition therapy can reduce the risk of complications (the risk of complications in experimental group VS control group is reduced by 19%, 22.9%VS26.9%) and the risk of death (the risk of death in experimental group VS control group is reduced by 35%, 7.2%VS9.9%).[5].

Tips: Oral Nutritional Supplements (ONS) are nutritional preparations that can provide a variety of macronutrients and micronutrients for oral use with the aim of increasing oral nutritional intake. ONS has many advantages such as balanced nutrition, scientific formula, safety, effectiveness, convenience and quickness.
Click to learn more about ONS.
2. ONS is the first choice of nutritional intervention for the elderly with comorbidity.
ONS is a way of enteral nutrition, which is usually used to supplement the intake when the food is not enough to meet the body’s needs. As a special nutritional supplement formula, ONS can strengthen the content of nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, fat, minerals and vitamins in food and provide balanced nutrients to meet the body’s needs for nutrients. ONS is safe, effective, economical and convenient, and it is the first choice of nutritional intervention for the elderly with comorbidity.

3. Under what circumstances do you need ONS intervention?
Standardized nutritional therapy is the guarantee for patients to benefit. According to the 2018ESPEN guidelines for nutritional support for comorbidity of internal medicine patients.[6]And guidelines for the application of parenteral and enteral nutrition in elderly patients in China (2020).[7]According to the recommendation, elderly patients with comorbidity need routine nutritional screening; MNA-SF and NRS2002 nutrition screening tools are recommended. Elderly patients with malnutrition or nutritional risk and normal or basically normal gastrointestinal function should start enteral nutrition therapy as soon as possible (within 48 hours) to improve muscle loss and nutritional supply, and ONS is the first choice for enteral nutrition.
4. Recommended usage and dosage
It was found that ONS with 400~600 kcal and/or 30g protein per day, taken orally for 30 ~ 90 days between meals, can improve the nutritional status and clinical outcome of elderly patients. Attention should be paid to frequency, temperature, speed and concentration during use. The temperature is about 40℃, and it will gradually increase from dilute to thick for the first time according to the patient’s intestinal adaptation.
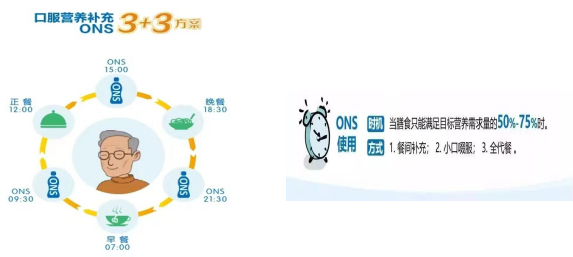
5. Precautions for Comorbid Patients to Use ONS
Guidelines recommend that comorbid patients should use a high-energy and high-protein diet to achieve energy and protein intake. High-quality protein, especially the formula rich in whey protein, is beneficial to the synthesis of protein in the elderly and easier to absorb; Long-term adequate dietary fiber intake is conducive to maintaining intestinal function. In clinical practice, according to different basic diseases, it is necessary to consider the specific nutrient composition, taste, texture and preservation of ONS. For example, the powder has a long shelf life and is ready to use, and the liquid formula has a high-energy and high-protein dosage form, which can be eaten immediately after opening, but the shelf life after opening is short. Specifically, it is necessary to focus on the patient’s compliance and the sustainability of improving nutritional status.
6. The key points of ONS formula selected by patients with different chronic diseases
According to the guidelines, the standard whole protein formula is suitable for most elderly patients. For elderly patients with chronic heart failure, high energy density formula is helpful for fluid management; For COPD patients with stable malnutrition, it is suggested to adopt a formula with higher fat ratio; The intake of protein is 1.5g/kg/d; Increasing omega-3 fatty acids and dietary fiber intake is beneficial to improve lung function and outcome; Elderly patients with diabetes can use the formula suitable for diabetes; For the nutritional treatment of elderly patients with high risk of pressure ulcers with nutritional risk or malnutrition, ONS with high protein is the first choice, and special nutrients rich in arginine, vitamin C and zinc can promote wound healing. In the elderly patients with sarcopenia who are at risk of malnutrition, vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids can improve the decline of muscle strength in the elderly and prevent falls.
The incidence of malnutrition in elderly patients with comorbidity is high and the harm is serious. Medical institutions and related professionals need to strengthen the training of standardized nutritional treatment, and families and society should give more support to ONS, such as raising awareness of nutritional treatment and supporting medical insurance policies, which will help improve the nutritional status of elderly patients and bring multiple benefits.
References:
1. Xu Hu, Li Fan, Cao Feng. Clinical challenges and coping strategies in the management of comorbidity in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Elderly Multiple Organ Diseases, 2019,18 (12), 942-946.
2. Cui Hongyuan, Zhu Mingwei, Chen Wei, et al. Multi-center investigation on nutritional status of elderly inpatients in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Geriatrics, 2021,03,364-369.
3. Kang Junren, Qiu Yue, Li Hailong, et al. Multi-center cross-sectional survey on nutritional risk of 3885 elderly people in China community [J]. Journal of China Academy of Medical Sciences, 2018,40 (05), 637-641.
4. Xu Mengqi, Qin Kan. Analysis of influencing factors of anticholinergic burden and malnutrition in elderly patients with comorbidity [J]. Zhongnan Pharmacy, 2022,20 (04), 934-938.
5.Schuetz P, Fehr R, Baechli V, et al. Individualised nutritional support in medical inpatients at nutritional risk: a randomised clinical trial [J]. Randomized Controlled Trial,Lancet. 2019 ; 393(10188):2312-2321.
6.Filomena Gomes , Philipp Schuetz , Lisa Bounoure , et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutritional support for polymorbid internal medicine patients[J]. Clin Nutr. 2018 ; 37(1):336-353.
7. Guidelines on Parenteral Enteral Nutrition for Elderly Patients in China (2020)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geriatrics, 2020,02: 119-132.
[Related links]
Topic-Super Doctor Says Nutrition
Source: Guangming Net












